Useful nutrients to deal with summer fatigue

Lying on a sunny beach, or cooling off by jumping in the pool, or even taking a walk in the mountains surrounded by nature, are just some of the activities that many of us love to do during Summertime.
In this season, exposure to heat causes severe symptoms, such as heat stroke – a condition which causes faintness, as well as dry, warm skin and sweating due to the inability of the body to control high temperatures. Other symptoms include swelling in the lower limbs, heat rash on the neck, cramps, headache, irritability, lethargy and weakness.
With sweat we lose numerous mineral salts and in the absence of these, some functions, such as muscle, are not able to take place correctly.
The most recommended advice is to drink plenty of water (minimum 2 liters per day) to replenish the minerals lost with sweat and eat seasonal fruits and vegetables as a source of energy and nutrients to face the typical heat of this season.
But if the feeling of tiredness and fatigue persists, what can we do?
In these cases, it may be useful to assume specifical food supplements, which can give adequate physical and mental energy, thanks to the synergistic action of substances with tonic-adaptogenic and energizing properties.

Energizing substances are able to increase the energy of the individual, already after a single intake. The generic term “energy” refers to both physical performance and the ability to concentrate and wake.
In this category we find Taurine, a sulfur amino acid that derives from the biosynthesis of two amino acids: cysteine and methionine. Taurine is very present in muscle tissues, where it plays an important role in muscle contraction, thanks to the regulation of calcium release at the level of the sarcoplasmic reticulum; it stimulates cardiac contraction activity during exercise, thus improving peripheral oxygenation and, in addition, inhibits the production and accumulation of lactic acid, promoting adequate muscle contraction.
Tonic substances are able to strengthen and invigorate various organs; their peculiarity is not to be affected by the negative rebound effect, which instead turns out to be common in stimulants, such as caffeine, which would make it necessary to take them frequently.
Adaptogenic substances, are very effective in increasing the recovery process after intense physical activity and allow the body to adapt to the stressful situation in which it finds itself. Tonics and adaptogens substances have in common the ability to improve the body’s energy production.
Among the substances with tonic-adaptogenic action we find Ginseng (Panax Ginseng). This plant contains ginsenosides, which have a positive action on the Central Nervous System. Therefore, ginseng increases the state of wakefulness and attention and also accelerates contractility and heart rate.
The synergistic effect of these substances brings an important benefit to combat situations of physical and mental fatigue in many conditions, such as weakness and fatigue due to the summer season.
In addition to supplementing the substances described above, in cases of physical fatigue, substances may be taken which promote normal muscle function, such as vitamin D, carnitine, arginine and magnesium.
The term vitamin D refers to a group of fat-soluble molecules of a steroid nature, responsible for the intestinal absorption of calcium, magnesium and phosphates and also involved in other biological functions. In fact, vitamin D doesn’t just keep bones healthy, but also acts as an immunostimulant, stimulating T-lymphocytes to defend us from pathogens, and also contributes to muscle contraction.
Carnitine is synthesized by human body from two amino acids: methionine and lysine; it exerts its action of transporting long-chain fatty acids inside the cells, at the mitochondrial level, where they are oxidized and converted into energy. Carnitine is not only used in sports to increase the strength of muscles, but is also used for its protective properties on the heart and blood vessels; in fact, it improves lipid structure by increasing HDL cholesterol levels and reducing circulating triglycerides.
Arginine is one of the 20 essential amino acids for human body, and its biological function consists in the production of nitric oxide at the level of blood vessels, which causing a vasodilation, allows a greater supply of oxygen and nutrients to the muscles. Arginine is particularly suitable for those who follow diets that do not include meat foods, such as vegan or vegetarian diets.
Magnesium is a macroelement that we have in quantities varying, between 22 and 26 g, and more than 50% is mineralized at the bone level. In our body, magnesium acts as a cofactor for more than 300 enzymes and is therefore involved in numerous biological processes, such as the synthesis of essential neurotransmitters at the central level and the production and release of cellular energy in the form of ATP (Adenosine triphosphate). Magnesium contributes to a reduction of tiredness and fatigue and to normal energy-yelding metabolism. It also, acting in balance with calcium, contributes to the normal muscle function, regulating muscle contraction, heartbeat, coagulation and blood pressure.
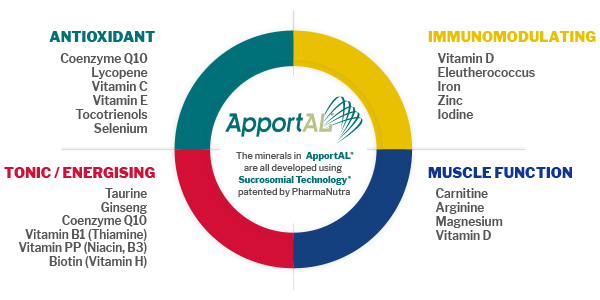
ApportAL® is a complete food supplement with 19 nutrients, that provides the energy necessary for the body to face all those situations related to the change of season or stressful periods that cause a sense of tiredness and physical and mental fatigue.
BIBLIOGRAPHY AND E SITOGRAPHY
- Kiefer, T. Pantuso. “Panax ginseng”. Am Fam Physician. 2003 Oct 15;68(8):1539-42.
- A. Silva; et al. “Taurine supplementation decreases oxidative stress in skeletal muscle after eccentric exercise” Cell Biochem Funct. Jan-Feb 2011;29(1):43-9. doi: 10.1002/cbf.1716. Epub 2010 Dec 27.
- https://www.who.int/health-topics/heatwaves
- Aranow C. “Vitamin D and the immune system.” J Investig Med. 2011 Aug;59(6):881-6. doi: 10.2310/JIM.0b013e31821b8755.
- Standing Committee on the Scientific Evaluation of Dietary Reference Intakes; Food and Nutrition Board; Institute of Medicine (IOM). Dietary Reference Intakes for Calcium, Phosphorus, Magnesium, Vitamin D, and Fluoride; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1997
